You must have seen real-time applications where data is changed frequently or updated in real-time, this happens because that application is using a WebSocket to achieve this functionality.
By the end of this article, you’ll able to learn:
- What is WebSocket?
- How to create a WebSocket server and client using Python?
What is WebSocket?
A WebSocket allows two-way communication (bidirectional) between two entities over a single TCP connection. This means a WebSocket client and server can interact with each other multiple times in a single connection.
A Websocket connection is a fully-duplex connection protocol which means the data can be sent and received simultaneously in both directions, keeping the connection alive until either server or client decides to stop the connection.
It is used in real-time applications to exchange low-latency data in both directions.
How to Create a WebSocket using Python
In this section, you will create a WebSocket server and client using Python. You will use Python’s websockets library to create a server and a client.
Install Dependency
Open your terminal window and run the following command:
|
1 |
pip install websockets |
Using the websockets library, you can create a websocket server and client in Python super easily.
Create a WebSocket Server
In this section, you’ll create a WebSocket server that will retrieve the values from the client and based on those values sends the appropriate response to the client.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
import websockets import asyncio # Creating WebSocket server async def ws_server(websocket): print("WebSocket: Server Started.") try: while True: # Receiving values from client name = await websocket.recv() age = await websocket.recv() # Prompt message when any of the field is missing if name == "" or age == "": print("Error Receiving Value from Client.") break # Printing details received by client print("Details Received from Client:") print(f"Name: {name}") print(f"Age: {age}") # Sending a response back to the client if int(age) < 18: await websocket.send(f"Sorry! {name}, You can't join the club.") else: await websocket.send(f"Welcome aboard, {name}.") except websockets.ConnectionClosedError: print("Internal Server Error.") async def main(): async with websockets.serve(ws_server, "localhost", 7890): await asyncio.Future() # run forever if __name__ == "__main__": asyncio.run(main()) |
The above code imports the websockets library for creating a WebSocket server and communicating with it and the asyncio library for making use of asynchronous tasks.
The code then defines an asynchronous function called ws_server() that takes WebSocket connection (websocket) as its parameter.
Inside the function, a try block is used that handles the incoming messages from the client. Within the try block, a while loop is created which means the code will run continuously.
Within the loop, the code receives two values from the client using the websocket.recv() and stores them within the name and age variables respectively. The code checks if any of the value is missing, if it is then it prompts a message and breaks the loops otherwise it proceeds and prints the values received from the client.
The code then sends the appropriate response back to the client based on the values it gets.
In the except block, the code handles any websockets.ConnectionClosedError exceptions that indicate an error occurred during the connection.
The code then defines another asynchronous function called main() that starts a WebSocket server. The WebSocket server is created using websockets.serve() method which listens on localhost and port 7890.
The server will run forever due to asyncio.Future(). This will keep the server alive and run continuously to listen to incoming messages.
In the end, the main() function is run using the asyncio.run(main()).
Create a WebSocket Client
In this section, you’ll create a client that takes the input from the user and displays the response sent by the WebSocket server.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
import websockets import asyncio # The main function that will handle connection and communication # with the server async def ws_client(): print("WebSocket: Client Connected.") url = "ws://127.0.0.1:7890" # Connect to the server async with websockets.connect(url) as ws: name = input("Your Name (type 'exit' to quit): ") if name == 'exit': exit() age = input("Your Age: ") # Send values to the server await ws.send(f"{name}") await ws.send(f"{age}") # Stay alive forever, listen to incoming msgs while True: msg = await ws.recv() print(msg) # Start the connection asyncio.run(ws_client()) |
The above code defines an asynchronous function called ws_client(). Inside the function, the WebSocket client is connected to the WebSocket server using the websockets.connect() method passed with the URL (ws://127.0.0.1:789) of the server created in the previous section.
The user is prompted to enter the name and if they type “exit”, the code quits the process. Then the user is asked to enter their age and both values (name and age) are sent to the WebSocket server using the ws.send() method.
After that, the code enters the infinite loop to continuously listen to the incoming messages from the server using the ws.recv() method. The message is then printed on the console.
Finally, the ws_client() function is run using asyncio.run(ws_client()). This will start the WebSocket client to accept the information from the user and display the response sent by the server.
Running the WebSocket Server and Client
You need to put the server and client code in two separate Python files. First, you need to run the WebSocket server script to start the server.
Open a terminal window, navigate to the project directory, and run the script file, in this case, the script is stored in the main.py Python file.
|
1 |
python main.py |
Now open another terminal window and run the WebSocket client script, in this case, the script is stored in the client.py file.
|
1 |
python client.py |
This will start the WebSocket client connected to the server. You will see the prompts asking for your name and age.
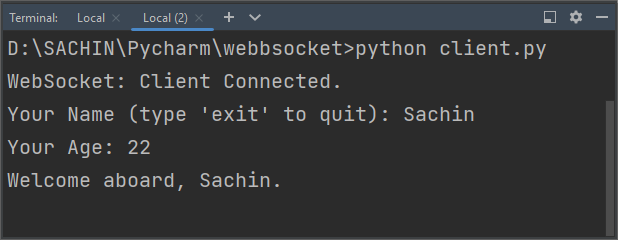
Here, "Sachin" and "22" are sent to the server, and in return, the server responds with the "Welcome aboard, Sachin" message on the console.
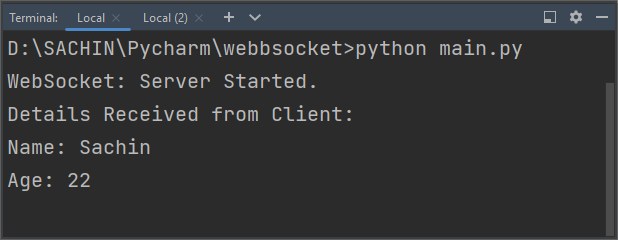
The information entered by the user will be displayed on the WebSocket server console. You can see this in the image below.
You can also run the client using the websockets interactive shell using the following command.
|
1 |
python -m websockets ws://localhost:7890 |
Conclusion
In this article, you learned to create a WebSocket server and client using the websockets library in Python. This technology is used in applications in which data changes in real-time.
Resource: https://websockets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/howto/quickstart.html
🏆Other articles you might be interested in if you liked this one
✅Create multi-threaded Python programs using a threading module.
✅What is the StandardScaler function in Machine Learning?
✅Upload and display images on the frontend using Flask.
✅What is Python coroutines and how to use it to execute tasks asynchronously?
✅How to use async/await in Python using the asyncio module?
✅How to create a database on Appwrite cloud using only Python.
That’s all for now
Keep Coding✌✌