FastAPI is a fast and modern web framework known for its support for asynchronous REST API and ease of use.
In this article, we’ll see how to stream videos on frontend in FastAPI.
StreamingResponse
Stream Local Video
FastAPI provides a StreamingResponse class that is dedicated to streaming purposes. The StreamingResponse class takes a generator or iterator and streams the response.
Here’s a simple example of streaming local video to the browser.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
# localvid.py from fastapi import FastAPI from fastapi.responses import StreamingResponse app = FastAPI() # Video path vid_path = 'sample_video.mp4' # Function to stream local video def stream_local_video(): with open(vid_path, 'rb') as vid_file: yield from vid_file # Path to stream video @app.get("/") def video_stream(): return StreamingResponse(stream_local_video(), media_type='video/mp4') |
We imported the StreamingResponse class from the fastapi.responses module.
In the video_stream() path operation function, we returned the response using StreamingResponse. We passed the generator function stream_local_video() and media_type as an argument to the StreamingResponse class.
The generator function stream_local_video() reads the bytes of the video and yield from iterates over the bytes and each part iterated is then yielded.
The following command will run the server and stream the video on http://127.0.0.1:8000/.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
> fastapi dev localvid.py ╭────────── FastAPI CLI - Development mode ───────────╮ │ │ │ Serving at: http://127.0.0.1:8000 │ │ │ │ API docs: http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs │ │ │ │ Running in development mode, for production use: │ │ │ │ fastapi run │ │ │ ╰─────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯ |
Stream Online Video
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
# onlinevid.py from fastapi import FastAPI from fastapi.responses import StreamingResponse import requests app = FastAPI() # Video URL vid_url = 'https://cdn.pixabay.com/video/2023/07/28/173530-849610807_large.mp4' # Function to stream online video def stream_online_video(url): response = requests.get(url, stream=True) for portion in response.iter_content(chunk_size=1024*1024): yield portion # Path to stream video @app.get("/") def video_stream(): return StreamingResponse(stream_online_video(vid_url), media_type='video/mp4') |
In this example, we used the requests library to fetch the content of the video from the URL and we set the stream=True (avoids reading the video at once into memory). Then we iterated and yielded the video content in chunks (1024 bytes at a time).
When we run the server, it will serve the video from the URL.
Instead of a hardcoded URL, we can specify the URL in the endpoint.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
from fastapi import FastAPI from fastapi.responses import StreamingResponse import requests app = FastAPI() # Function to stream online video def stream_online_video(url): response = requests.get(url, stream=True) for portion in response.iter_content(chunk_size=1024*1024): yield portion # Path to stream video @app.get("/") def video_stream(url): return StreamingResponse(stream_online_video(url), media_type='video/mp4') |
In this example, we modified the path operation function video_stream() to accept a URL.
Now we can specify the URL of the video in the endpoint in the following format.
http://127.0.0.1:8000/?url=https://cdn.pixabay.com/video/2023/07/28/173530-849610807_large.mp4
We can also make the path operation function asynchronous using
async.
FileResponse
Stream Local Video
The FileResponse class simply takes a file and streams the response.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
from fastapi import FastAPI from fastapi.responses import FileResponse app = FastAPI() # Video path vid_path = 'video.mp4' # Path to stream video @app.get("/") def video_stream(): return FileResponse(vid_path, media_type='video/mp4') |
In the above example, we simply passed a video file in the FileResponse class and returned the response.
We didn’t read and iterate over the bytes of the video to stream it like we did in the case of StreamingResponse.
The FileResponse class is ideal for relatively small or medium-sized files as it loads the file in the memory. Large files will consume more memory.
Stream Online Video
Streaming video from the URL using FileResponse isn’t the same as streaming the local video. As we know, the FileResponse class takes a file and streams it.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
from fastapi import FastAPI from fastapi.responses import FileResponse import requests import os app = FastAPI() # Video URL vid_url = 'https://cdn.pixabay.com/video/2023/07/28/173530-849610807_large.mp4' local_vid = 'sample_video.mp4' # Function to save video from URL def save_as_file(url, path): if not os.path.exists(path): response = requests.get(url) with open('sample_video.mp4', 'wb') as vid: vid.write(response.content) save_as_file(vid_url, local_vid) # Path to stream video @app.get("/") def video_stream(): return FileResponse(local_vid, media_type='video/mp4') |
In this example, instead of streaming the local video, we streamed the video from the URL using FileResponse.
This isn’t the best practice because we first saved the video from the URL in the local machine and then streamed the video.
The FileResponse class can be best utilized for local files, not web content.
That was all about streaming video directly to the browser but we don’t want to do that every time, instead, we want the video to be streamed on our website’s landing page.
Stream Video on Frontend
So, how to stream video on the frontend using FastAPI? We need to create a frontend using HTML and then stream the video.
First, create a directory named serve_video or whatever you want to name it, and create the following files and sub-directories.
|
1 2 3 4 |
serve_video/ - templates/ - display_video.html - app.py |
The app.py file will contain our backend code and the display_video.html file will contain frontend code.
app.py
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request from fastapi.responses import StreamingResponse, HTMLResponse from fastapi.templating import Jinja2Templates import requests app = FastAPI() templates = Jinja2Templates(directory="templates") vid_urls = [ "https://cdn.pixabay.com/video/2023/07/28/173530-849610807_large.mp4", 'https://cdn.pixabay.com/video/2024/03/31/206294_large.mp4', 'https://cdn.pixabay.com/video/2023/10/11/184510-873463500_large.mp4', 'https://cdn.pixabay.com/video/2023/06/17/167569-837244635_large.mp4' ] # Stream the video from the URL def stream_video(url): response = requests.get(url, stream=True) for portion in response.iter_content(chunk_size=1024*1024): yield portion # Endpoint to render the HTML template with the video player @app.get("/", response_class=HTMLResponse) async def video_template(request: Request): return templates.TemplateResponse("display_video.html", {"request": request}) # Endpoint to stream the video @app.get("/video/{video_id}") async def video_stream(vid_id: int): if 0 <= vid_id < len(vid_urls): return StreamingResponse(stream_video(vid_urls[vid_id]), media_type="video/mp4") else: return HTMLResponse("Video not found", status_code=404) |
In this example, we are streaming multiple videos on the frontend. We have a list of video URLs stored within vid_urls.
We have a stream_video() generator function that yields the video in smaller chunks.
We created an asynchronous path operation function video_template() that returns a response from HTML (@app.get("/", response_class=HTMLResponse)) file.
We are serving HTML from a template stored within the templates directory, so, we set up a Jinja2 template directory where HTML templates are stored (templates = Jinja2Templates(directory="templates")). This is where FastAPI will look for .html files.
Note: To render templates in FastAPI, you need to install the Jinja2 (pip install jinja2) library.
Then we returned the response using templates.TemplateResponse("display_video.html", {"request": request}). We passed our HTML template display_video.html and along with it, a dictionary containing Request object ({"request": request}). This Request object provides information about the incoming HTTP request, such as headers, cookies, and URLs, which can be accessed within the HTML template.
Next, we created an endpoint (@app.get("/video/{video_id}")) to stream individual videos based on the ID in the vid_ulrs. The video_stream(vid_id: int) path operation functions accept the index of the video in vid_urls.
Within the video_stream(), the if condition checks if the vid_id is within the range, if not, then raises an error otherwise the video is streamed based on the specified index.
display_video.html
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Stooooockzz</title> </head> <body> <h1>What we do?</h1> <p>We create awesome stock videos for free usage</p> <h3>Video Samples</h3> <div style="display: flex; justify-content: space-evenly;"> <video width='20%' height='30%' style="border-radius: 10px;" controls autoplay> <source src="/video/0" type="video/mp4"> </video> <video width='20%' height='30%' style="border-radius: 10px;" controls autoplay> <source src="/video/1" type="video/mp4"> </video> <video width='20%' height='30%' style="border-radius: 10px;" controls autoplay> <source src="/video/2" type="video/mp4"> </video> <video width='20%' height='30%' style="border-radius: 10px;" controls autoplay> <source src="/video/3" type="video/mp4"> </video> </div> </body> </html> |
This HTML file contains multiple <video> tags with the source pointing to the /video/{video_id} endpoint that streams the video based on ID.
Here, we passed <source src="/video/0" type="video/mp4"> within the <video> tag that represents streaming the first video from the vid_urls (in app.py) list. Similarly, we specified the same source but changed the ID within each <video> tag.
|
1 |
> fastapi dev app.py |
Upon running the server using the above command, we get the following response on the frontend.
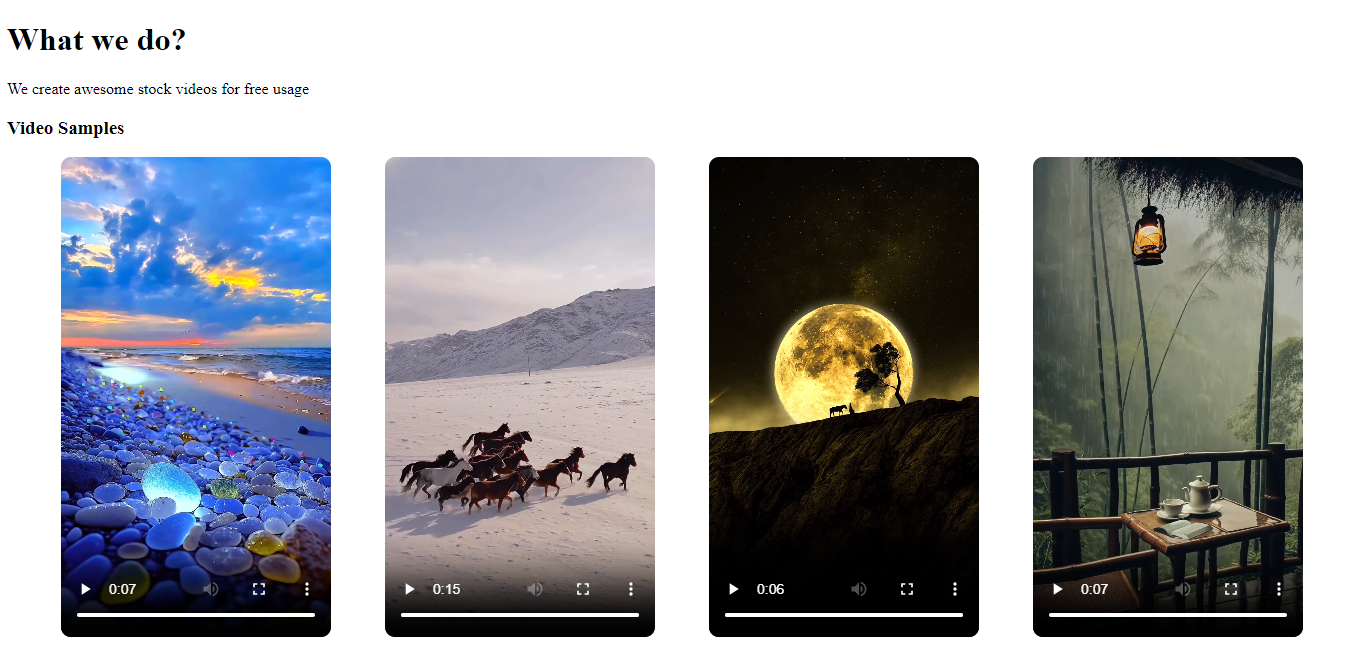
Conclusion
We’ve used StreaminResponse and FileResponse classes to stream local and web videos directly on the browser, and along with this we’ve also streamed multiple videos using StreamingResponse which was rendered using HTML files on the browser.
In this article, we’ve used URLs of the video residing on the internet but you can also fetch URLs from databases, local files, disks, etc.
That’s all for now.
Keep Coding✌✌.