We all have ever encountered the term OOPs (Object-Oriented Programming) in programming. OOP is an integral part of any programming language that helps carry out complex concepts. It provides a way to structure and organize the code in such a manner that makes it easier to maintain and scale the code.
Classes are an essential concept in OOP or we can say that classes are the building blocks of Object-Oriented Programming which is a programming model based on objects and classes.
Object-Oriented Programming has four important concepts and one of them is inheritance.
What is Inheritance?
Inheritance can be defined as the mechanism that permits the newly created classes to inherit the methods and attributes of the existing class or parent class. The classes that inherit the methods and attributes from the parent class are called subclass and the existing class is called a superclass.
As soon as a subclass inherits the superclass, it gains all of the methods and attributes of the superclass. This allows us to reuse the code as well as we can extend or modify the behavior of the superclass.
For example-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
class Hero: def power(self): print("Rich") class Ironman(Hero): def speciality(self): print("Genius", "Millionaire", "Playboy", "Philanthropist") obj = Ironman() obj.power() obj.speciality() |
The class Hero has a method power that returns a specific power a hero has. Then we created a subclass Ironman that inherits the superclass Hero and the subclass Ironman has its own method speciality that specifies the specialties of Ironman.
The subclass Ironman now has access to all the attributes and methods of the superclass Hero as well.
We accessed the method power using the class Ironman which inherited the method power from the class Hero.
|
1 2 |
Rich Genius Millionaire Playboy Philanthropist |
Inheritance helps us reduce the effort that we put into writing the same logic again and again and makes it easy to maintain and update the code.
Different types of inheritance:
- Single Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
Single Inheritance
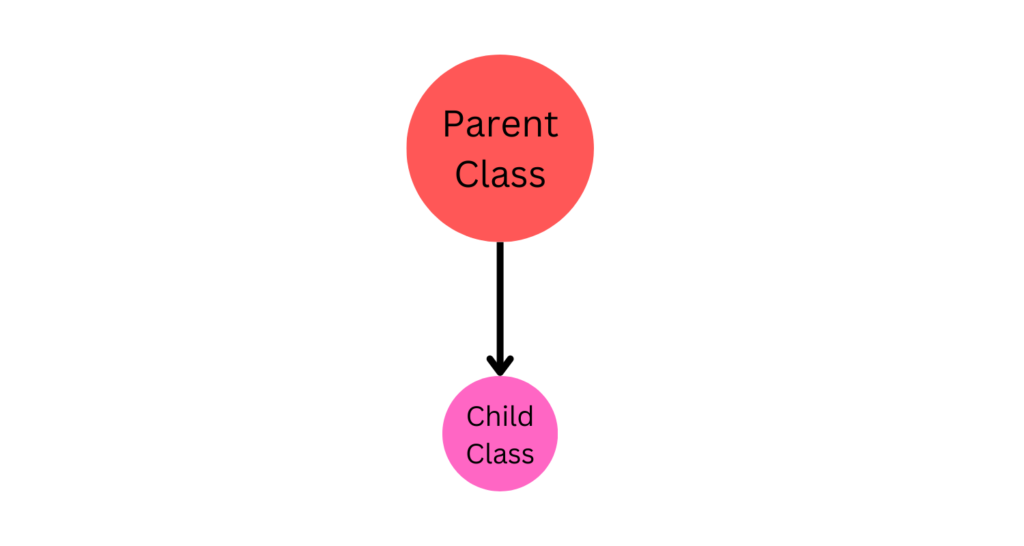
Single inheritance can be defined as an inheritance where a subclass or derived class inherits from a single superclass or parent class.
In simple words, the derived class or subclass has only one direct parent class. Here is an example of single inheritance.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# Parent or Base Class class Calculate: def sum(self, a, b): print(a + b) # Subclass or Derived Class class Number(Calculate): pass obj = Number() obj.sum(8, 90) ---------- 98 |
The above code is no different from the code that we discussed earlier where we saw the first glimpse of class inheritance in Python.
The subclass Number inherited the superclass Calculate and now the methods inside it can now be accessed by the subclass Number. We created the instance for the subclass Number and then accessed the sum function from the superclass or parent class Calculate.
Using constructor
Until now, we saw a simple demonstration of the class inheritance in which a subclass gains the methods and attributes of the superclass by just passing it as an argument.
Now we’ll see how to perform inheritance when a class has a constructor function.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
# Base class class Hero: # Constructor function def __init__(self, reel_name, hero_name): self.reel_name = reel_name self.hero_name = hero_name def show(self): print(self.reel_name) print(self.hero_name) # Derived class class Name(Hero): def __init__(self, real_name, reel_name, hero_name): self.real_name = real_name # Calling the __init__ of the parent class Hero.__init__(self, reel_name, hero_name) def display(self): print(self.real_name) Hero.show(self) obj = Name("RDJ", "Tony Stark", "IronMan") obj.display() print("-"*20) obj.show() |
In the above code, we created the base class Hero and inside it, we defined the constructor function that takes two arguments reel_name and hero_name and then we defined the function show that prints the reel_name and hero_name.
Then we created a subclass Name that inherits the superclass Hero and then we created a constructor function that takes three arguments real_name, reel_name, and hero_name.
In order to access the objects of the parent class Hero, we invoked __init__ of the parent class Hero and passed the required arguments.
Next, we created a function display that prints the real_name and calls the function show from the class Hero.
Then we created obj an instance of the class Name and called the function display and show.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
RDJ Tony Stark IronMan -------------------- Tony Stark IronMan |
What if we didn’t call the __init__ of the parent class?
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
class Cal: def __init__(self, a, b): self.a = a self.b = b def sq(self): print(self.a ** self.b) class X(Cal): def __init__(self, c): self.c = c obj = X("Hello") obj.sq() |
We have done everything similar to what we did earlier but this time we didn’t call the __init__ of the parent class Cal and tried to call the function sq from it.
|
1 2 3 4 |
Traceback (most recent call last): ... print(self.a ** self.b) AttributeError: 'X' object has no attribute 'a' |
We encountered an error and this happened because the objects of the parent class Cal were not available for the subclass or child class X.
Multiple Inheritance

Python supports multiple-class inheritance and can be defined as an inheritance where a subclass or child class inherits from more than one superclass.
In short, a subclass has more than one direct parent class or superclass. Let’s understand the concept of multiple-class inheritance with an example.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
# First Parent Class class First: def __init__(self): self.greet = "Hello" # Second Parent Class class Second: def __init__(self): self.name = "Geeks" # Child or Derived Class class Child(First, Second): def __init__(self): First.__init__(self) Second.__init__(self) def combine(self): print(self.greet, self.name) print("Welcome to GeekPython.") obj = Child() obj.combine() |
In the above code, subclass Child inherited two superclasses named First and Second that will help gain the attributes of both superclasses inside the subclass Child.
We then created a function combine that prints the values of self.greet and self.name and a string. We created obj which is an instance of the class and then called the combine function.
|
1 2 |
Hello Geeks Welcome to GeekPython. |
Note: There is a risk of using multiple inheritances because it can lead to uncertainty in the code and also cause a “Diamond Problem” where a subclass inherits certain conflicting methods from multiple parent classes.
Diamond Problem
The “Diamond Problem” often occurs primarily in the case of multiple inheritance where a subclass inherits the conflicting methods from the multiple superclasses that eventually create ambiguity in the code.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
# Base Class class Hello: def func(self): print("Hello") # Derived Class class Geek(Hello): def func(self): print("Geeks") # Derived Class class Python(Hello): def func(self): print("GeekPython") # Derived Class class GeekPython(Geek, Python): pass obj = GeekPython() obj.func() |
In the above code, subclasses Geek and Python inherit from the superclass Hero and then another subclass GeekPython inherits from the subclasses Geek and Python. They all have a function with the same name func.
Now when we call the func, the order of the parent class decides from which class GeekPython inherits from. So, in this case, the function func inside the class Geek will get executed.
|
1 |
Geeks |
If we change the order of the class, then we’ll get the following output.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# Derived Class class GeekPython(Python, Geek): pass ---------- GeekPython |
Multi-level Inheritance

Multi-level inheritance can be defined as where a subclass inherits from the single subclass and then another subclass inherits from the first subclass. By this, the second subclass can access all the attributes and methods from both the first subclass and the superclass.
Let’s understand with an example showing multi-level inheritance.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
# Base Class class GrandPa: def __init__(self): self.age = 100 # Derived CLass class Parent(GrandPa): def __init__(self): self.name = "Geek" GrandPa.__init__(self) # Derived Class class GrandChild(Parent): def __init__(self): self.hobby = "Gaming" Parent.__init__(self) def display(self): print("Grandpa:", self.age) print("Parent:", self.name) print("Grandchild:", self.hobby) obj = GrandChild() obj.display() |
In the above code, the subclass Parent inherits from the superclass GrandPa and now the first subclass Parent has access to the methods of the superclass GrandPa.
Then another subclass GrandChild inherited from the first subclass Parent and it has access to the methods that both the first subclass and superclass have.
|
1 2 3 |
Grandpa: 100 Parent: Geek Grandchild: Gaming |
Hierarchical Inheritance

Hierarchical inheritance can be defined as when more than one derived class inherits from a single base class. Let’s understand with an example.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
# Base Class class Calculate: def __init__(self, a, b): self.a = a self.b = b def division(self): print(self.a / self.b) # Derived Class class Add(Calculate): def __init__(self, a, b): Calculate.__init__(self, a, b) def add(self): print("Addition:", self.a + self.b) Add.division(self) # Derived Class class Subtract(Calculate): def __init__(self, a, b): Calculate.__init__(self, a, b) def subtract(self): print("Subtraction:", self.a - self.b) Subtract.division(self) obj1 = Add(34, 98) obj2 = Subtract(45, 67) obj1.add() obj2.subtract() |
In the above code, both derived class Add and Subtract inherited from the superclass or base class Calculate.
|
1 2 3 4 |
Addition: 132 0.3469387755102041 Subtraction: -22 0.6716417910447762 |
Hybrid Inheritance

This type of inheritance is a blend of different inheritance which means it has a combination of two different types of inheritance like multiple or multi-level inheritances or multiple or single inheritances.
Here is an example showing the demonstration of hybrid inheritance.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
# Base Class class Role: def role(self): print("Protagonist") # Derived Class class Luffy(Role): def power(self): print("Gum-Gum devil fruit") # Derived Class class Naruto(Role): def power1(self): print("Nine-tail fox") # Derived Class class Anime(Luffy, Naruto): def anime(self): print("They are anime characters.") obj = Anime() obj.role() obj.power() print("-"*20) obj.role() obj.power1() print("-"*20) obj.anime() |
In the above code, the subclasses Luffy and Naruto inherit from the superclass Role and then the subclass Anime inherits from the subclasses Luffy and Naruto.
The first scenario where Luffy and Naruto inherit from the superclass Role shows the single inheritance and the second scenario where Anime inherits from the subclasses Luffy and Naruto shows the multiple inheritances.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Protagonist Gum-Gum devil fruit -------------------- Protagonist Nine-tail fox -------------------- They are anime characters. |
Conclusion
Inheritance is one of the pillars of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) that allows a new class to inherit the methods and attributes of an existing class or parent class.
Python is one of the programming languages that support multiple inheritance of the class but it could lead to uncertainty in the code.
Let’s review what we’ve learned:
We saw the concepts of different types of inheritance in Python:
- Single Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Multi-level Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
🏆Other articles you might like if you like this article
✅Public, Protected and Private access modifiers in Python.
✅Build your own API in Python using FastAPI in a few steps.
✅A modern way to perform string interpolation in Python.
✅Build your own CLI in Python using the argparse module.
✅Different ways to remove whitespaces from the string in Python.
✅Bitwise operators explained with examples in Python.
That’s all for now
Keep Coding✌✌